Are you struggling to get the most out of your seated cable row exercise? You’re not alone! This common problem often stems from poor form during the exercise. While it may seem simple enough, there are many components to the seated cable row that can be tricky to master. But fear not! In this post, we’ll go over step-by-step how to perform the seated cable row properly so you can maximize your gains and see that back grow!
Seated Cable Row Summary
- Primary Muscles: Deltoid – Posterior
- Secondary Muscles: Brachialis, Brachioradialis, Pectoralis Major – Sternal
- Equipment: Cable Machine with Straight Bar and Bench
- Mechanics Type: Compound
- Force: Pull
- Utility: Basic or Auxiliary
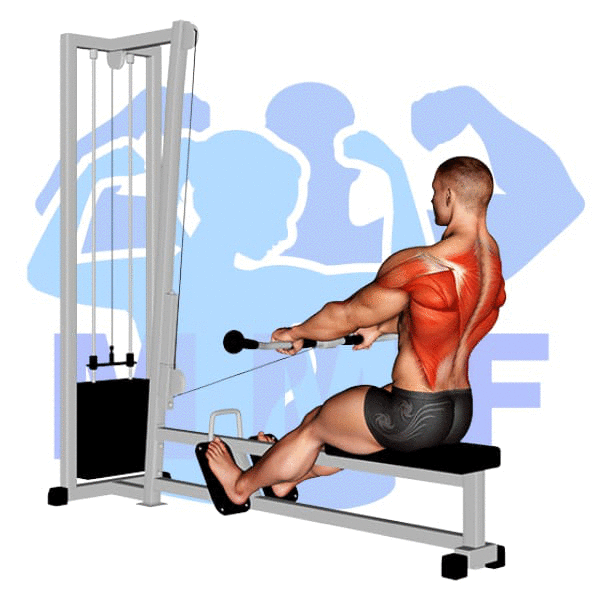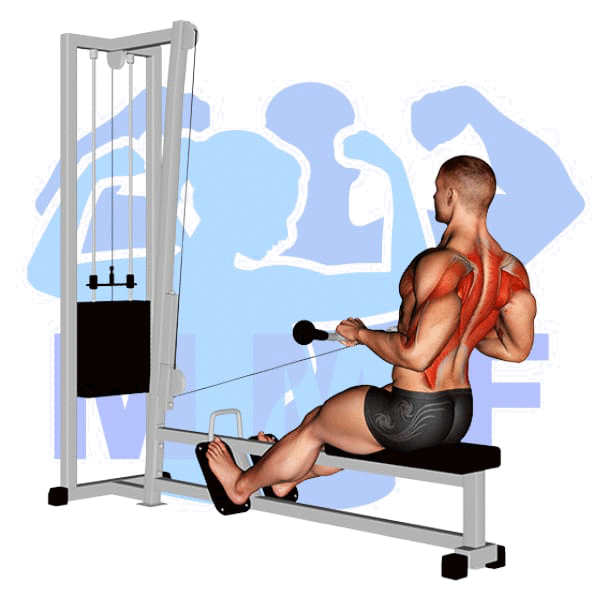
Seated Cable Row Instructions
- Sit forward on the seat or bench to grab the cable bar.
- Next, place your feet on the foot support.
- Then, slide your hips back, positioning your knees with a slight bend.
- Pull the bar to your waist while straightening the lower back.
- Keep pulling with your shoulders back while pushing your chest forward and arching your back.
- Finally, allow the cable to extend your arms, stretching your shoulders forward, but keeping your lower back flexed.
- Repeat the seated cable rows for 6-12 repetitions.
Video Tutorial
Seated Cable Row Muscles
Target (Agonist)
- Deltoid – Posterior
- Erector Spinae
- Infraspinatus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Rhomboids
- Teres Major
- Teres Minor
- Trapezius
Synergists
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Pectoralis Major – Sternal
Dynamic Stabilizers
- Biceps Brachii
- Triceps – Long Head
Stabilizers
Antagonist Stabilizers
- None

Benefits of Seated Cable Row
The seated cable row is an effective exercise for targeting the posterior deltoid muscle, a key muscle in the shoulder area. This exercise helps to strengthen the posterior deltoid, which is important for improving posture, stability, and overall shoulder strength. Additionally, this exercise can help to improve scapular stability and control, which can lead to improved shoulder function. By incorporating the seated cable row into a regular strength training or fitness routine, individuals can benefit from increased strength and stability in the shoulders and upper back, as well as improved posture.
Tips for Performing Seated Cable Row
Your at the right place if you’re motivated to advance your seated cable row execution. These tips can allow you to fully benefit from this wonderful workout and make the best of its results. You can develop your upper back muscles, and even lower your chances of experiencing an injury. Let’s get started and take a look at how these suggestions will benefit you.
- Keep your spine straight: Make sure to keep your back straight and shoulders back during the exercise. This will help to engage the back muscles and reduce strain on the spine.
- Don’t swing: Avoid using momentum to lift the weight and instead focus on using the back muscles. This will help to target the correct muscles and ensure that you’re getting the most out of the exercise.
- Use a slow tempo: The slower you move through the exercise, the more you’ll be able to engage your back muscles, which will help you get fit faster.
Benefits and Tips Video
Frequent Mistakes To Avoid
Staying away from errors can be the difference between a productive workout and an injury when performing seated cable row. Moreover, achieving the most out of the exercise requires appropriate technique, and avoiding perform typical mistakes can allow you to perform the exercise correctly and obtain optimal results. But relax, it’s not quite as difficult as it might seem. By knowing the errors to avoid and taking the appropriate actions, you may complete the exercise securely and successfully. Then let’s begin on avoiding those common errors and making this exercise a normal part of your strength training.
- Not keeping the back straight: When performing the Seated Cable Row, it is important to keep the back straight. Doing so prevents any strain on the spine and ensures that the exercise is performed correctly and safely.
- Not engaging the core: Engaging the core is an important step in the Seated Cable Row. Not doing so can lead to an unstable posture, which can cause injuries and also diminish the results of the exercise.
- Performing too many repetitions: Performing too many repetitions of the Seated Cable Row can lead to muscle fatigue and overtraining. It is important to perform a moderate number of repetitions in order to get the best results from the exercise and to avoid any potential injuries.
Find More Cable Exercises Here
Variations and Complementary Exercises
The Seated Cable Row is a great exercise for building back strength, but sometimes it’s nice to have some options. Here are some variations, complementary, or alternative exercises that work similar muscles:
Smith Machine Bent Over Row

The Smith Machine Bent Over Row is a great complementary or alternative exercise for the Seated Cable Row. This exercise works the back muscles in a similar fashion to the Seated Cable Row, but with the addition of stability provided by the Smith Machine. The Bent Over Row forces the lifter to use more control and stability in the movement, which can help to build greater strength and muscle activation. Additionally, this exercise can be done with a much heavier weight than the Seated Cable Row, allowing for more effective muscle overload and hypertrophy.
Band Rear Deltoid Row

The band rear deltoid row is a great alternative or complementary exercise for the seated cable row. This exercise is great for targeting the rear deltoids, trapezius muscles, and rhomboids. It can be done with a resistance band anchored to a wall or a door frame. To perform the exercise, start by standing with your feet hip-width apart and the band in both hands. With your arms extended, pull the band towards your body while squeezing your shoulder blades together. Hold for a few seconds and then slowly release your arms back to the starting position. This exercise can help improve shoulder strength and mobility, making it a great addition to any workout routine.
Barbell Pendlay Row

The Barbell Pendlay Row is an excellent alternative or complementary exercise to the Seated Cable Row. It is a compound, multi-joint exercise that targets the back muscles, specifically the lats, rhomboids, and mid-back muscles. It also works the biceps and core muscles. The exercise is performed by bending over at the waist and gripping a barbell with an overhand grip, then pulling the barbell up to the chest in a rowing motion. The barbell should remain close to the body throughout the exercise and you should focus on squeezing the shoulder blades together at the top of the movement. This exercise is great for targeting the mid-back muscles, which are often neglected when performing Seated Cable Rows.
Check Out These Top Cable Exercises
Barbell Rear Delt Row

The Barbell Rear Delt Row is a great complementary or alternative exercise to the Seated Cable Row. This exercise involves bending over at the waist while holding a barbell in front of you with an overhand grip. You then row the barbell up and back towards your torso while squeezing your shoulder blades together. This exercise helps to strengthen your back and rear deltoids, which can help you perform Seated Cable Rows more effectively. Additionally, it helps increase your range of motion and stability in the back and shoulders, allowing for greater gains in overall strength.
Dumbbell Supported One Arm Row

The Dumbbell Supported One Arm Row is a great complementary or alternative exercise to the Seated Cable Row. This exercise focuses on strengthening the back muscles while still working the arms and chest. It requires the use of a bench and dumbbell, making it an accessible and convenient exercise for those with limited equipment. The exercise can be completed with one arm at a time, allowing for increased focus on form and muscle isolation. It also allows for greater range of motion, as the user can pull further back than with the Seated Cable Row. In addition, it helps to improve posture and balance due to the unilateral movement.
Inverted Row Underhand Grip

The Inverted Row Underhand Grip is a great complementary or alternative exercise to the Seated Cable Row. It is an upper-body pulling exercise that targets the back muscles, and it can be done with a barbell, rings, or TRX suspension trainer. The inverted row underhand grip puts more emphasis on the lower lats than the seated cable row, but both exercises will help strengthen and build the back. Both exercises also involve scapular retraction, which is important for good posture and preventing shoulder pain. The inverted row underhand grip is an excellent exercise for those who want to build their upper body strength without putting too much strain on their lower back.
Find More Back Exercises Here
Opposing Complementary Exercises
It is important to round out your workout by engaging opposing muscle groups. To ensure that your body is balanced and you are working your muscles evenly, try incorporating the following exercises into your workout routine in addition to the Seated Cable Row.
Barbell Wide Reverse Grip Bench Press

The Barbell Wide Reverse Grip Bench Press is an excellent complement to the Seated Cable Row exercise. It works the opposing muscle group of the back, specifically targeting the chest and front of the shoulder muscles. This exercise helps to build strength and size of the pectoral muscles and shoulders, allowing for greater overall muscle development. By performing this exercise in conjunction with the Seated Cable Row, you can create a balanced workout that strengthens both your back and chest muscles.
Barbell Guillotine Bench Press

The Barbell Guillotine Bench Press is a great exercise for strengthening the chest muscles. By performing this exercise, the chest muscles are being worked in a different way than the Seated Cable Row, which works the back muscles. This allows for a more balanced strength training program as it is utilizing the opposing muscle groups. The Barbell Guillotine Bench Press targets the chest and shoulder muscles, while the Seated Cable Row targets the back and arm muscles. This combination helps to build a stronger and more balanced physique.
Barbell Decline Wide Grip Press

The barbell decline wide grip press is a great complementary exercise to the seated cable row as it works the opposing muscle group. The decline press specifically targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps muscles while the seated cable row focuses on the back muscles. The combination of these two exercises can help build both strength and stability in the upper body. Additionally, when done correctly, this combination can help improve posture and overall balance in the body.
Row Your Way to a Stronger Upper Body!
Building a strong upper body not only helps you perform daily tasks with ease, but it also improves your posture and overall aesthetically pleasing appearance. Seated cable row is a great exercise that targets the upper back muscles, biceps, and forearms, aiding in their growth and development. It requires minimal equipment and can easily be modified to suit your fitness level, making it a go-to exercise for many gym-goers. Incorporating seated cable row into your workout routine can help you achieve a stronger, more defined upper body.
References: Wikipedia | ExRx.net | PubMed.gov | Comprehensive List of Back Cable Exercises




